 Structure Learning
Structure Learning
# 1. Structured Learning
# 1.1 什么是 Structured Learning
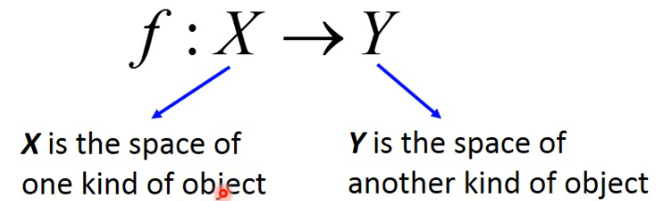
We need a more powerful function
- input and output are both objects with structures.
- Object: sequence, list, tree, bounding box …
# 1.2 Example Application
- Speech recognition
- X: Speech signal (sequence) –> Y: text (sequence)
- Translation
- X: Mandarin sentence (sequence) –> Y: English sentence (sequence)
- Syntactic Parsing
- X: Sentence –> Y: parsing tree (tree structure)
- Object Detection
- X: image –> Y: bounding box
- Summarization
- X: long document –> Y: summary (short paragraph)
- Retrieval
- X: keyword –> Y: search result (a list of webpage)
# 2. Unified Framework
# 2.1 Structured Learning 的 Unified Framework
Structured Learning 的做法听上去可能很难,但他有一个 unified framework:
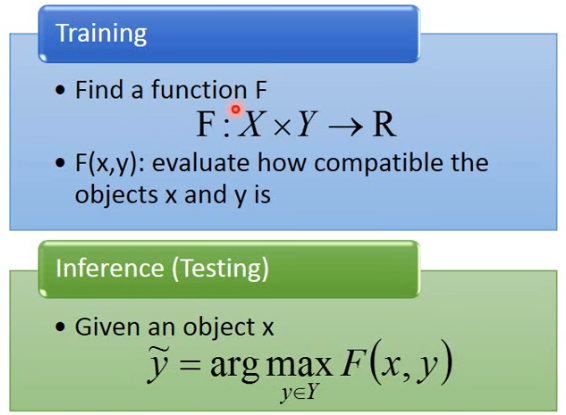
在 training 阶段,我们首先要找一个大小的 F,它的 input 是 x 与 y,它的 output 就是一个 real number,F 做得事情就是衡量两个 structured object
在 inference 阶段,给一个新的 x,我们要穷举所有可能的 y,然后代入 F 中,看看哪个 y 的 F(x, y) 最大,让 F 值最大的 y 就记作
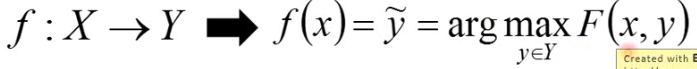
# 2.2 Example - Object Detection
Task description:
- Using a bounding box to highlight the position of a certain object in an image.
- E.g. A detector of Haruhi

# 1)Training 阶段
这个 Object Detection 该怎么做呢?在 training 阶段:
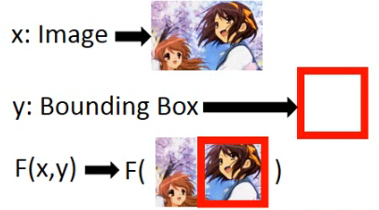
那这里的 F(x, y) 所做的就是去说这张 image 与这个 bounding box 有多匹配,如下图所示:
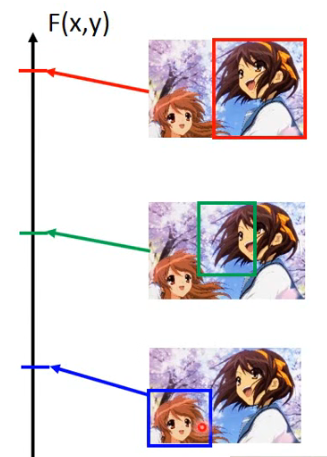
- bounding box 框在了凉宫春日上的话,得分就很高,越偏离,得分就越低。
# 2)Inference 阶段
比如我们 input 下面一张 image:

然后我们穷举所有的 bounding box
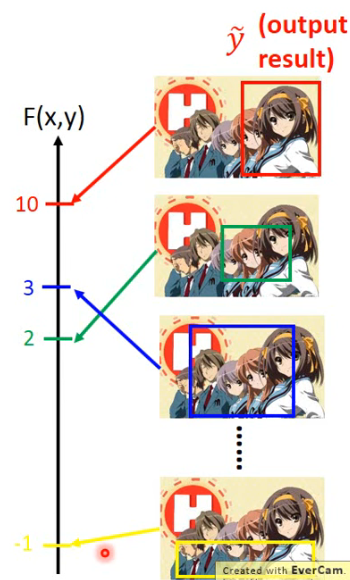
那我们最终的 output
# 2.3 Unified Framework 到底在搞什么?
第一次听这个 Unified Framework 也许不知道在搞什么,也许感觉这个 F 很怪,但换一个说法也许就可以接受了:
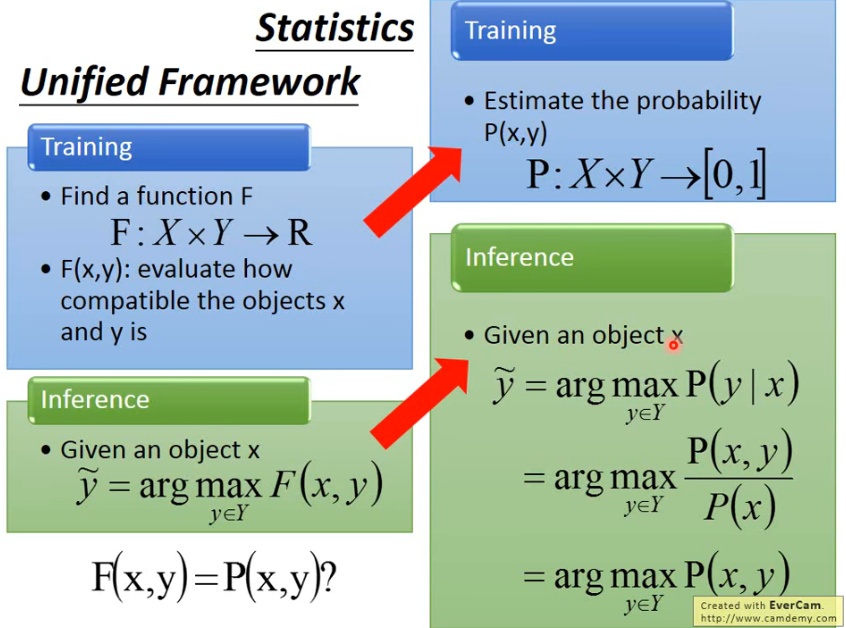
- Training 阶段,我们就 estimate 一个 x 和 y 的 joint probability
- Inference 阶段,给我们一个 object
所以刚刚 Unified Framework 中说的 F 所计算 x 与 y 有多相容,其实就是在说计算 x 与 y 的 joint probability,因为其实这个几率
概率图模型(Graphical Model)就是 structured learning 的一种,完全可以套进来。像 Markov Random Field 等,它们都是去找一个 evaluation 的 function
用概率
- Probability cannot explain everything. 比如在 Retrieval 的任务中,input x 是查询词 keyword,y 是搜寻的结果 webpage,而衡量这个 keyword 与 webpage 共同出现的几率,会让人觉得很怪;
- 0-1 constraint is not necessary. x 和 y 都是 structured object,它们的取值空间都是一个很大的 space,而做这个几率就需要 normalize 成一个 0-1 的东西,而这个 normalization 就需要你花很大的时间
用概率也有好处的:
- Meaningful. 用几率是比较容易让你去想象
structured learning 也有人同时提出另一种叫法:Energy-based Model,可以参考 http://www.cs.nyu.edu/~yann/research/ebm/
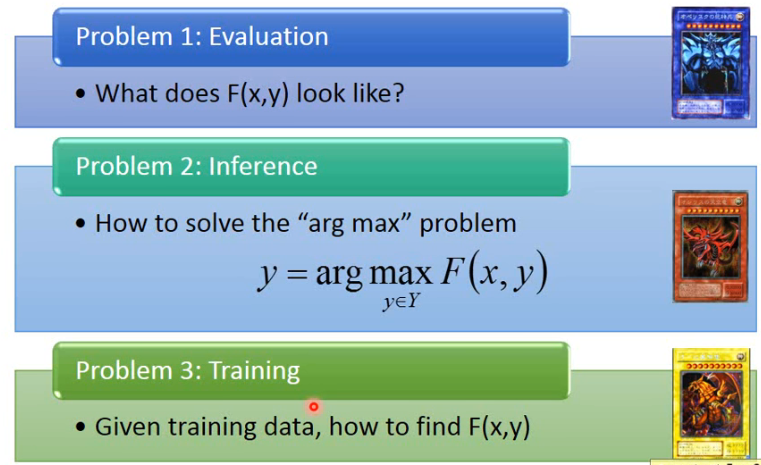
# 3. Three Problem
具体做这个 Unified Framework,你就要去解三个 problem:
# 3.1 Problem 1
Evaluation:What does F(x, y) look like?
- How
比如在下面这些具体任务中,F(x, y) 应该长什么样是一个 problem:

# 3.2 Problem 2
Inference:How to solve the "arg max" problem?
- The space Y can be extremely large!
例如:

# 3.3 Problem 3
Training:Given training data, how to learn F(x, y)
- Principle:正确的 (x, y) 的 pair 的得分应该大于其他的。
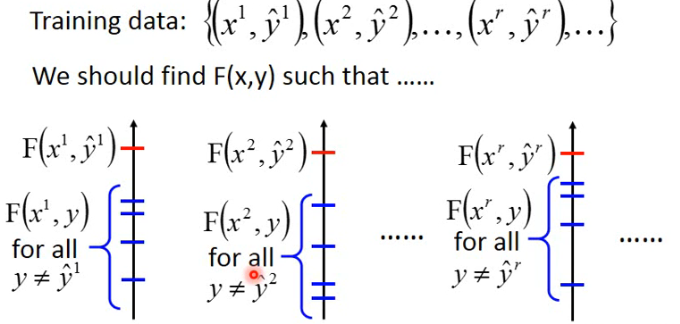
解出这三个 problem,你就可以做 structured learning 的 problem:
# 3.4 与其他 model 的关系
Have you heard the three problems elsewhere?
- 在解 HMM 问题时,就是说有三个 problem 要去解,其实那就是与这里的是一样的
- 这其实也可以与 DNN link 到一起
怎样与 DNN link 到一起呢?如下图:
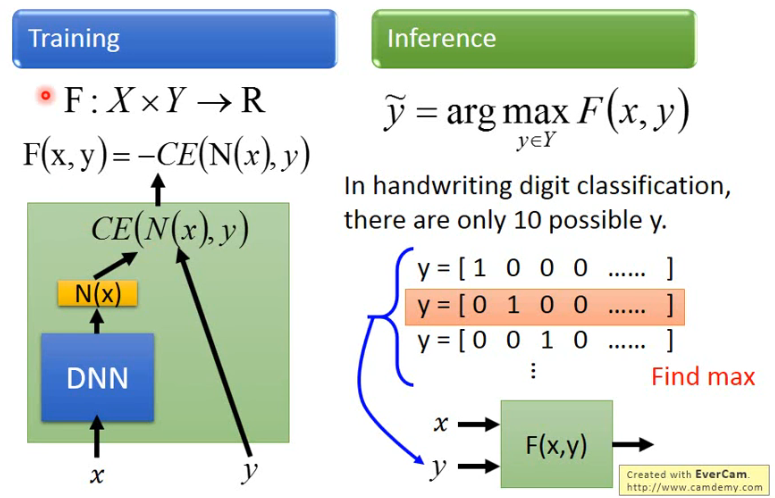
- 在手写数字辨识中,x 是 image,经过 DNN 得到 N(x),然后拿他与 y 计算 cross-entropy,得到 CE(N(x), y),那么 structured learning 中的 Unified Framework 的 F 就是 -CE(N(x), y) 了。
# 4. Structured Linear Model
# 4.1 Problem 1
Evaluation:What does F(x, y) look like?
对于 (x, y),我们要给出一系列的 feature,这里每一个
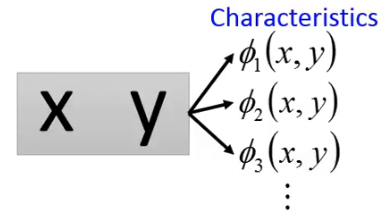
然后我们的 F(x, y) 就可以写成下面这种形式:

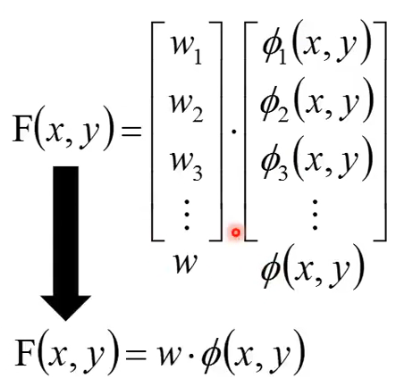
写成 vector 的形式可以将 F(x, y) 写成如下的形式:
以 Object Detection 为例,那 image 和 bounding box 是一个 (x, y) pair:
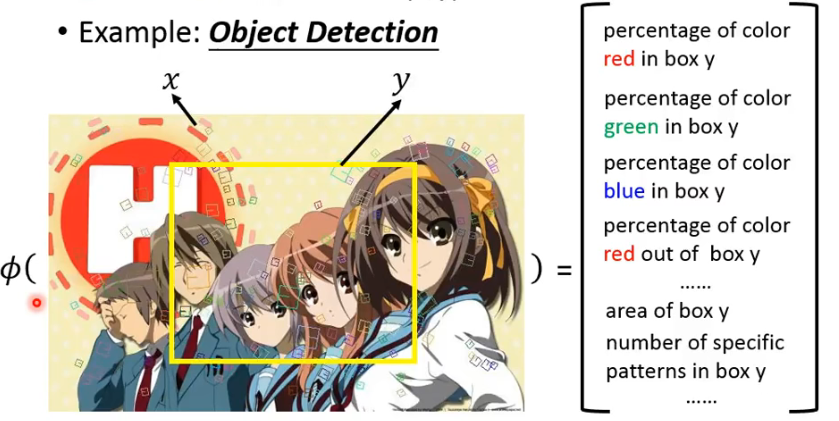
- 这个例子中,它们的 feature 就可以自己来选了,最终这些 feature 组成了
刚刚这个抽出 feature 是通过人工的方式,但这往往不太好,这种抽取 feature 的方式是可以交给 network 来完成:
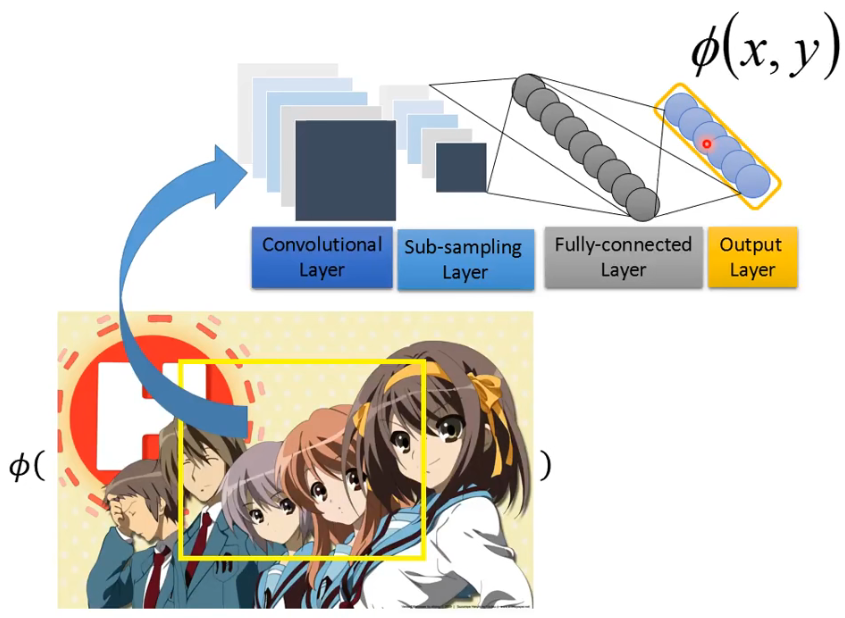
上面是以 object detection 为例,下面以 Summarization 为例:
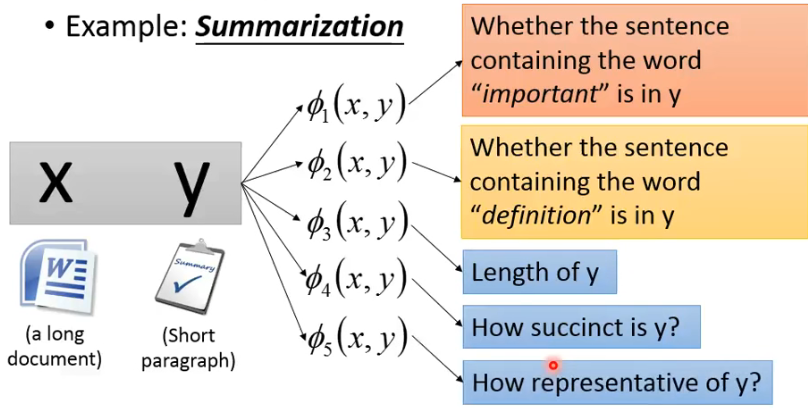
- 当然,也可以让 deep neural network 来抽取一些有用的 features
# 4.2 Problem 2
Inference:How to solve the "arg max" problem?
我们先假装我们已经解决这个问题了
# 4.3 Problem 3
Training:Given training data, how to learn F(x, y)
由于

- 也就是说,我们想要找的 w 是能够让 training example 的得分大过 incorrect example 的得分。示例如下:
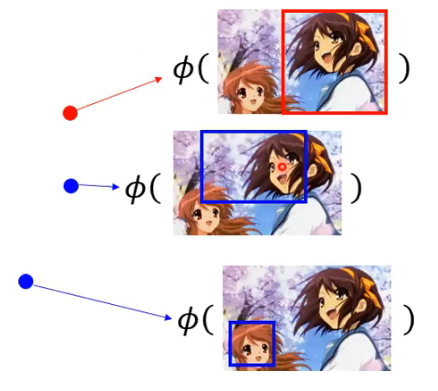
这个要找的 w 是什么样子呢?让
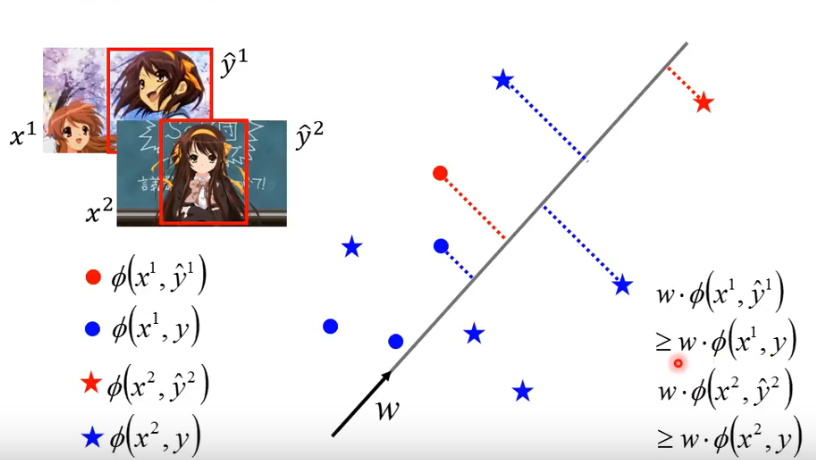
- 圈圈只和圈圈比,星星只和星星比
# 4.4 Solution of Problem 3
Difficult? Not as difficult as expected! 下面提供一个演算法来做这件事,只要红色的这个存在,那这个演算法就可以找到答案。

- 对每一个 training example
这个算法的过程其实很像 perceptron,perceptron 做的是 binary classification,而今天这个做的是 structure learning。
关于这个 algorithm 的运行示例可以参考 https://www.bilibili.com/video/BV13x411v7US/?p=33 (opens new window)
可以证明,这个演算法最终是可以收敛的,是可以结束的,具体数学证明可以参考原视频。
